Mark `-1` as an available niche for file descriptors
Based on discussion from <https://internals.rust-lang.org/t/can-the-standard-library-shrink-option-file/12768>, the file descriptor `-1` is chosen based on the POSIX API designs that use it as a sentinel to report errors. A bigger niche could've been chosen, particularly on Linux, but would not necessarily be portable.
This PR also adds a test case to ensure that the -1 niche (which is kind of hacky and has no obvious test case) works correctly. It requires the "upper" bound, which is actually -1, to be expressed in two's complement.
The equivalent of `std::fs::read_to_string`, but generalized to all
`Read` impls.
As the documentation on `std::io::read_to_string` says, the advantage of
this function is that it means you don't have to create a variable first
and it provides more type safety since you can only get the buffer out
if there were no errors. If you use `Read::read_to_string`, you have to
remember to check whether the read succeeded because otherwise your
buffer will be empty.
It's friendlier to newcomers and better in most cases to use an explicit
return value instead of an out parameter.
Move {f32,f64}::clamp to core.
`clamp` was recently stabilized (tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/44095). But although `Ord::clamp` was added in `core` (because `Ord` is in `core`), the versions for the `f32` and `f64` primitives were added in `std` (together with `floor`, `sin`, etc.), not in `core` (together with `min`, `max`, `from_bits`, etc.).
This change moves them to `core`, such that `clamp` on floats is available in `no_std` programs as well.
Stabilize all stable methods of `Ipv4Addr`, `Ipv6Addr` and `IpAddr` as const
This PR stabilizes all currently stable methods of `Ipv4Addr`, `Ipv6Addr` and `IpAddr` as const.
Tracking issue: #76205
`Ipv4Addr` (`const_ipv4`):
- `octets`
- `is_loopback`
- `is_private`
- `is_link_local`
- `is_multicast`
- `is_broadcast`
- `is_docmentation`
- `to_ipv6_compatible`
- `to_ipv6_mapped`
`Ipv6Addr` (`const_ipv6`):
- `segments`
- `is_unspecified`
- `is_loopback`
- `is_multicast`
- `to_ipv4`
`IpAddr` (`const_ip`):
- `is_unspecified`
- `is_loopback`
- `is_multicast`
## Motivation
The ip methods seem like prime candidates to be made const: their behavior is defined by an external spec, and based solely on the byte contents of an address. These methods have been made unstable const in the beginning of September, after the necessary const integer arithmetic was stabilized.
There is currently a PR open (#78802) to change the internal representation of `IpAddr{4,6}` from `libc` types to a byte array. This does not have any impact on the constness of the methods.
## Implementation
Most of the stabilizations are straightforward, with the exception of `Ipv6Addr::segments`, which uses the unstable feature `const_fn_transmute`. The code could be rewritten to equivalent stable code, but this leads to worse code generation (#75085).
This is why `segments` gets marked with `#[rustc_allow_const_fn_unstable(const_fn_transmute)]`, like the already const-stable `Ipv6Addr::new`, the justification being that a const-stable alternative implementation exists https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/76206#issuecomment-685044184.
## Future posibilities
This PR const-stabilizes all currently stable ip methods, however there are also a number of unstable methods under the `ip` feature (#27709). These methods are already unstable const. There is a PR open (#76098) to stabilize those methods, which could include const-stabilization. However, stabilizing those methods as const is dependent on `Ipv4Addr::octets` and `Ipv6Addr::segments` (covered by this PR).
Add the "async" and "promise" doc aliases to `core::future::Future`
Adds the "async" and "promise" doc aliases to `core::future::Future`. This enables people who search for "async" or "promise" to find `Future`, which is Rust's core primitive for async programming. Thanks!
Stabilize or_insert_with_key
Stabilizes the `or_insert_with_key` feature from https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/71024. This allows inserting key-derived values when a `HashMap`/`BTreeMap` entry is vacant.
The difference between this and `.or_insert_with(|| ... )` is that this provides a reference to the key to the closure after it is moved with `.entry(key_being_moved)`, avoiding the need to copy or clone the key.
Edit formatting in Rust Prelude docs
Use consistent punctuation and capitalization in the list of things re-exported in the prelude.
Also adds a (possibly missing) word.
Refactor and fix `parse_prefix` on Windows
This PR is an extension of #78692 as well as a general refactor of `parse_prefix`:
**Fixes**:
There are two errors in the current implementation of `parse_prefix`:
Firstly, in the current implementation only `\` is recognized as a separator character in device namespace prefixes. This behavior is only correct for verbatim paths; `"\\.\C:/foo"` should be parsed as `"C:"` instead of `"C:/foo"`.
Secondly, the current implementation only handles single separator characters. In non-verbatim paths a series of separator characters should be recognized as a single boundary, e.g. the UNC path `"\\localhost\\\\\\C$\foo"` should be parsed as `"\\localhost\\\\\\C$"` and then `UNC(server: "localhost", share: "C$")`, but currently it is not parsed at all, because it starts being parsed as `\\localhost\` and then has an invalid empty share location.
Paths like `"\\.\C:/foo"` and `"\\localhost\\\\\\C$\foo"` are valid on Windows, they are equivalent to just `"C:\foo"`.
**Refactoring**:
All uses of `&[u8]` within `parse_prefix` are extracted to helper functions and`&OsStr` is used instead. This reduces the number of places unsafe is used:
- `get_first_two_components` is adapted to the more general `parse_next_component` and used in more places
- code for parsing drive prefixes is extracted to `parse_drive`
Add fast futex-based thread parker for Windows.
This adds a fast futex-based thread parker for Windows. It either uses WaitOnAddress+WakeByAddressSingle or NT Keyed Events (NtWaitForKeyedEvent+NtReleaseKeyedEvent), depending on which is available. Together, this makes this thread parker work for Windows XP and up. Before this change, park()/unpark() did not work on Windows XP: it needs condition variables, which only exist since Windows Vista.
---
Unfortunately, NT Keyed Events are an undocumented Windows API. However:
- This API is relatively simple with obvious behaviour, and there are several (unofficial) articles documenting the details. [1]
- parking_lot has been using this API for years (on Windows versions before Windows 8). [2] Many big projects extensively use parking_lot, such as servo and the Rust compiler itself.
- It is the underlying API used by Windows SRW locks and Windows critical sections. [3] [4]
- The source code of the implementations of Wine, ReactOs, and Windows XP are available and match the expected behaviour.
- The main risk with an undocumented API is that it might change in the future. But since we only use it for older versions of Windows, that's not a problem.
- Even if these functions do not block or wake as we expect (which is unlikely, see all previous points), this implementation would still be memory safe. The NT Keyed Events API is only used to sleep/block in the right place.
[1]\: http://www.locklessinc.com/articles/keyed_events/
[2]\: https://github.com/Amanieu/parking_lot/commit/43abbc964e
[3]\: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/archive/msdn-magazine/2012/november/windows-with-c-the-evolution-of-synchronization-in-windows-and-c
[4]\: Windows Internals, Part 1, ISBN 9780735671300
---
The choice of fallback API is inspired by parking_lot(_core), but the implementation of this thread parker is different. While parking_lot has no use for a fast path (park() directly returning if unpark() was already called), this implementation has a fast path that returns without even checking which waiting/waking API to use, as the same atomic variable with compatible states is used in all cases.
doc(array,vec): add notes about side effects when empty-initializing
Copying some context from a conversation in the Rust discord:
* Both `vec![T; 0]` and `[T; 0]` are syntactically valid, and produce empty containers of their respective types
* Both *also* have side effects:
```rust
fn side_effect() -> String {
println!("side effect!");
"foo".into()
}
fn main() {
println!("before!");
let x = vec![side_effect(); 0];
let y = [side_effect(); 0];
println!("{:?}, {:?}", x, y);
}
```
produces:
```
before!
side effect!
side effect!
[], []
```
This PR just adds two small notes to each's documentation, warning users that side effects can occur.
I've also submitted a clippy proposal: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/issues/6439
Link loop/for keyword
Even though the reference already have all of these, I am just adding related keywords in the see also to let others easily click on the related keyword.
Windows TLS: ManuallyDrop instead of mem::forget
The Windows TLS implementation still used `mem::forget` instead of `ManuallyDrop`, leading to the usual problem of "using" the `Box` when it should not be used any more.
Dogfood `str_split_once()`
Part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/74773.
Beyond increased clarity, this fixes some instances of a common confusion with how `splitn(2)` behaves: the first element will always be `Some()`, regardless of the delimiter, and even if the value is empty.
Given this code:
```rust
fn main() {
let val = "...";
let mut iter = val.splitn(2, '=');
println!("Input: {:?}, first: {:?}, second: {:?}", val, iter.next(), iter.next());
}
```
We get:
```
Input: "no_delimiter", first: Some("no_delimiter"), second: None
Input: "k=v", first: Some("k"), second: Some("v")
Input: "=", first: Some(""), second: Some("")
```
Using `str_split_once()` makes more clear what happens when the delimiter is not found.
Make the kernel_copy tests more robust/concurrent.
These tests write to the same filenames in /tmp and in some cases these files don't get cleaned up properly. This caused issues for us when different users run the tests on the same system, e.g.:
```
---- sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy stdout ----
thread 'sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: Os { code: 13, kind: PermissionDenied, message: "Permission denied" }', library/std/src/sys/unix/kernel_copy/tests.rs:71:10
---- sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy stdout ----
thread 'sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: Os { code: 13, kind: PermissionDenied, message: "Permission denied" }', library/std/src/sys/unix/kernel_copy/tests.rs💯10
```
Use `std::sys_common::io__test::tmpdir()` to solve this.
CC ``@the8472.``
Improve documentation for `std::{f32,f64}::mul_add`
Makes it more clear that performance improvement is not guaranteed when using FMA, even when the target architecture supports it natively.
Enforce no-move rule of ReentrantMutex using Pin and fix UB in stdio
A `sys_common::ReentrantMutex` may not be moved after initializing it with `.init()`. This was not enforced, but only stated as a requirement in the comments on the unsafe functions. This change enforces this no-moving rule using `Pin`, by changing `&self` to a `Pin` in the `init()` and `lock()` functions.
This uncovered a bug I introduced in #77154: stdio.rs (the only user of ReentrantMutex) called `init()` on its ReentrantMutexes while constructing them in the intializer of `SyncOnceCell::get_or_init`, which would move them afterwards. Interestingly, the ReentrantMutex unit tests already had the same bug, so this invalid usage has been tested on all (CI-tested) platforms for a long time. Apparently this doesn't break badly on any of the major platforms, but it does break the rules.\*
To be able to keep using SyncOnceCell, this adds a `SyncOnceCell::get_or_init_pin` function, which makes it possible to work with pinned values inside a (pinned) SyncOnceCell. Whether this function should be public or not and what its exact behaviour and interface should be if it would be public is something I'd like to leave for a separate issue or PR. In this PR, this function is internal-only and marked with `pub(crate)`.
\* Note: That bug is now included in 1.48, while this patch can only make it to ~~1.49~~ 1.50. We should consider the implications of 1.48 shipping with a wrong usage of `pthread_mutex_t` / `CRITICAL_SECTION` / .. which technically invokes UB according to their specification. The risk is very low, considering the objects are not 'used' (locked) before the move, and the ReentrantMutex unit tests have verified this works fine in practice.
Edit: This has been backported and included in 1.48. And soon 1.49 too.
---
In future changes, I want to push this usage of Pin further inside `sys` instead of only `sys_common`, and apply it to all 'unmovable' objects there (`Mutex`, `Condvar`, `RwLock`). Also, while `sys_common`'s mutexes and condvars are already taken care of by #77147 and #77648, its `RwLock` should still be made movable or get pinned.
Based on discussion from https://internals.rust-lang.org/t/can-the-standard-library-shrink-option-file/12768,
the file descriptor -1 is chosen based on the POSIX API designs that use it as a sentinel to report errors.
A bigger niche could've been chosen, particularly on Linux, but would not necessarily be portable.
This PR also adds a test case to ensure that the -1 niche
(which is kind of hacky and has no obvious test case) works correctly.
It requires the "upper" bound, which is actually -1, to be expressed in two's complement.
implement better availability probing for copy_file_range
Followup to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/75428#discussion_r469616547
Previously syscall detection was overly pessimistic. Any attempt to copy to an immutable file (EPERM) would disable copy_file_range support for the whole process.
The change tries to copy_file_range on invalid file descriptors which will never run into the immutable file case and thus we can clearly distinguish syscall availability.
ext/ucred: Support PID in peer creds on macOS
This is a follow-up to https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/75148 (RFC: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/42839).
The original PR used `getpeereid` on macOS and the BSDs, since they don't (generally) support the `SO_PEERCRED` mechanism that Linux supplies.
This PR splits the macOS/iOS implementation of `peer_cred()` from that of the BSDs, since macOS supplies the `LOCAL_PEERPID` sockopt as a source of the missing PID. It also adds a `cfg`-gated tests that ensures that platforms with support for PIDs in `UCred` have the expected data.
Use is_write_vectored to optimize the write_vectored implementation for BufWriter
In case when the underlying writer does not have an efficient implementation `write_vectored`, the present implementation of
`write_vectored` for `BufWriter` may still forward vectored writes directly to the writer depending on the total length of the data. This misses the advantage of buffering, as the actually written slice may be small.
Provide an alternative code path for the non-vectored case, where the slices passed to `BufWriter` are coalesced in the buffer before being flushed to the underlying writer with plain `write` calls. The buffer is only bypassed if an individual slice's length is at least as large as the buffer.
Remove a FIXME comment referring to #72919 as the issue has been closed with an explanation provided.
The code in io::stdio before this change misused the ReentrantMutexes,
by calling init() on them and moving them afterwards. Now that
ReentrantMutex requires Pin for init(), this mistake is no longer easy
to make.
Fix incorrect io::Take's limit resulting from io::copy specialization
The specialization introduced in #75272 fails to update `io::Take` wrappers after performing the copy syscalls which bypass those wrappers. The buffer flushing before the copy does update them correctly, but the bytes copied after the initial flush weren't subtracted.
The fix is to subtract the bytes copied from each `Take` in the chain of wrappers, even when an error occurs during the syscall loop. To do so the `CopyResult` enum now has to carry the bytes copied so far in the error case.
Provide IntoInnerError::into_parts
Hi. This is an updated version of the IntoInnerError bits of my previous portmanteau MR #78689. Thanks to `@jyn514` and `@m-ou-se` for helpful comments there.
I have made this insta-stable since it seems like it will probably be uncontroversial, but that is definitely something that someone from the libs API team should be aware of and explicitly consider.
I included a tangentially-related commit providing documentation of the buffer full behaviiour of `&mut [u8] as Write`; the behaviour I am documenting is relied on by the doctest for `into_parts`.
In particular, IntoIneerError only currently provides .error() which
returns a reference, not an owned value. This is not helpful and
means that a caller of BufWriter::into_inner cannot acquire an owned
io::Error which seems quite wrong.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
If something goes wrong, one might want to unpeel the layers of nested
Writers to perform recovery actions on the underlying writer, or reuse
its resources.
`into_inner` can be used for this when the inner writer is still
working. But when the inner writer is broken, and returning errors,
`into_inner` simply gives you the error from flush, and the same
`Bufwriter` back again.
Here I provide the necessary function, which I have chosen to call
`into_raw_parts`.
I had to do something with `panicked`. Returning it to the caller as
a boolean seemed rather bare. Throwing the buffered data away in this
situation also seems unfriendly: maybe the programmer knows something
about the underlying writer and can recover somehow.
So I went for a custom Error. This may be overkill, but it does have
the nice property that a caller who actually wants to look at the
buffered data, rather than simply extracting the inner writer, will be
told by the type system if they forget to handle the panicked case.
If a caller doesn't need the buffer, it can just be discarded. That
WriterPanicked is a newtype around Vec<u8> means that hopefully the
layouts of the Ok and Err variants can be very similar, with just a
boolean discriminant. So this custom error type should compile down
to nearly no code.
Signed-off-by: Ian Jackson <ijackson@chiark.greenend.org.uk>
Use more std:: instead of core:: in docs for consistency
``@rustbot`` label T-doc
Some cleanup work to use `std::` instead of `core::` in docs as much as possible. This helps with terminology and consistency, especially for newcomers from other languages that have often heard of `std` to describe the standard library but not of `core`.
Edit: I also added more intra doc links when I saw the opportunity.
These tests write to the same filenames in /tmp and in some cases these
files don't get cleaned up properly. This caused issues for us when
different users run the tests on the same system, e.g.:
```
---- sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy stdout ----
thread 'sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: Os { code: 13, kind: PermissionDenied, message: "Permission denied" }', library/std/src/sys/unix/kernel_copy/tests.rs:71:10
---- sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy stdout ----
thread 'sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: Os { code: 13, kind: PermissionDenied, message: "Permission denied" }', library/std/src/sys/unix/kernel_copy/tests.rs💯10
```
Use `std::sys_common::io__test::tmpdir()` to solve this.
unix: Extend UnixStream and UnixDatagram to send and receive file descriptors
Add the functions `recv_vectored_fds` and `send_vectored_fds` to `UnixDatagram` and `UnixStream`. With this functions `UnixDatagram` and `UnixStream` can send and receive file descriptors, by using `recvmsg` and `sendmsg` system call.
std::io: Use sendfile for UnixStream
`UnixStream` was forgotten in #75272 .
Benchmark yields the following results.
Before:
`running 1 test
test sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_uds_copy ... bench: 54,399 ns/iter (+/- 6,817) = 2409 MB/s`
After:
`running 1 test
test sys::unix::kernel_copy::tests::bench_file_to_uds_copy ... bench: 18,627 ns/iter (+/- 6,007) = 7036 MB/s`
Rename `optin_builtin_traits` to `auto_traits`
They were originally called "opt-in, built-in traits" (OIBITs), but
people realized that the name was too confusing and a mouthful, and so
they were renamed to just "auto traits". The feature flag's name wasn't
updated, though, so that's what this PR does.
There are some other spots in the compiler that still refer to OIBITs,
but I don't think changing those now is worth it since they are internal
and not particularly relevant to this PR.
Also see <https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/131828-t-compiler/topic/opt-in.2C.20built-in.20traits.20(auto.20traits).20feature.20name>.
r? `@oli-obk` (feel free to re-assign if you're not the right reviewer for this)
Fix typo in `keyword` docs for traits
This PR fixes a small typo in the `keyword_docs.rs` file, describing the differences between the 2015 and 2018 editions of traits.
They were originally called "opt-in, built-in traits" (OIBITs), but
people realized that the name was too confusing and a mouthful, and so
they were renamed to just "auto traits". The feature flag's name wasn't
updated, though, so that's what this PR does.
There are some other spots in the compiler that still refer to OIBITs,
but I don't think changing those now is worth it since they are internal
and not particularly relevant to this PR.
Also see <https://rust-lang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/131828-t-compiler/topic/opt-in.2C.20built-in.20traits.20(auto.20traits).20feature.20name>.
Drop support for all cloudabi targets
`cloudabi` is a tier-3 target, and [it is no longer being maintained upstream][no].
This PR drops supports for cloudabi targets. Those targets are:
* aarch64-unknown-cloudabi
* armv7-unknown-cloudabi
* i686-unknown-cloudabi
* x86_64-unknown-cloudabi
Since this drops supports for a target, I'd like somebody to tag `relnotes` label to this PR.
Some other issues:
* The tidy exception for `cloudabi` crate is still remained because
* `parking_lot v0.9.0` and `parking_lot v0.10.2` depends on `cloudabi v0.0.3`.
* `parking_lot v0.11.0` depends on `cloudabi v0.1.0`.
[no]: https://github.com/NuxiNL/cloudabi#note-this-project-is-unmaintained
Stabilize `IpAddr::is_ipv4` and `is_ipv6` as const
Insta-stabilize the methods `is_ipv4` and `is_ipv6` of `std::net::IpAddr` as const, in the same way as [PR#76198](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/76198).
Possible because of the recent stabilization of const control flow.
Part of #76225 and #76205.
Insta-stabilize the methods `is_ipv4` and `is_ipv6` of `IpAddr`.
Possible because of the recent stabilization of const control flow.
Also adds a test for these methods in a const context.
Do what write does and optimize for the most likely case:
slices are much smaller than the buffer. If a slice does not fit
completely in the remaining capacity of the buffer, it is left out
rather than buffered partially. Special treatment is only left for
oversized slices that are written directly to the underlying writer.
Now that BufWriter always claims to support vectored writes,
look through it at the wrapped writer to decide whether to
use vectored writes for LineWriter.
If the underlying writer does not support efficient vectored output,
do it differently: always try to coalesce the slices in the buffer
until one comes that does not fit entirely. Flush the buffer before
the first slice if needed.
Stabilize clamp
Tracking issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/44095
Clamp has been merged and unstable for about a year and a half now. How do we feel about stabilizing this?
std: Update the bactrace crate submodule
This commit updates the `library/backtrace` submodule which primarily
pulls in support for split-debuginfo on macOS, avoiding the need for
`dsymutil` to get run to get line numbers and filenames in backtraces.
rustc_expand: Mark inner `#![test]` attributes as soft-unstable
Custom inner attributes are feature gated (https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/54726) except for attributes having name `test` literally, which are not gated for historical reasons.
`#![test]` is an inner proc macro attribute, so it has all the issues described in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/54726 too.
This PR gates it with the `soft_unstable` lint.
This commit updates the `library/backtrace` submodule which primarily
pulls in support for split-debuginfo on macOS, avoiding the need for
`dsymutil` to get run to get line numbers and filenames in backtraces.
unix/weak: pass arguments to syscall at the given type
Given that we know the type the argument should have, it seems a bit strange not to use that information.
r? `@m-ou-se` `@cuviper`
Add lint for panic!("{}")
This adds a lint that warns about `panic!("{}")`.
`panic!(msg)` invocations with a single argument use their argument as panic payload literally, without using it as a format string. The same holds for `assert!(expr, msg)`.
This lints checks if `msg` is a string literal (after expansion), and warns in case it contained braces. It suggests to insert `"{}", ` to use the message literally, or to add arguments to use it as a format string.
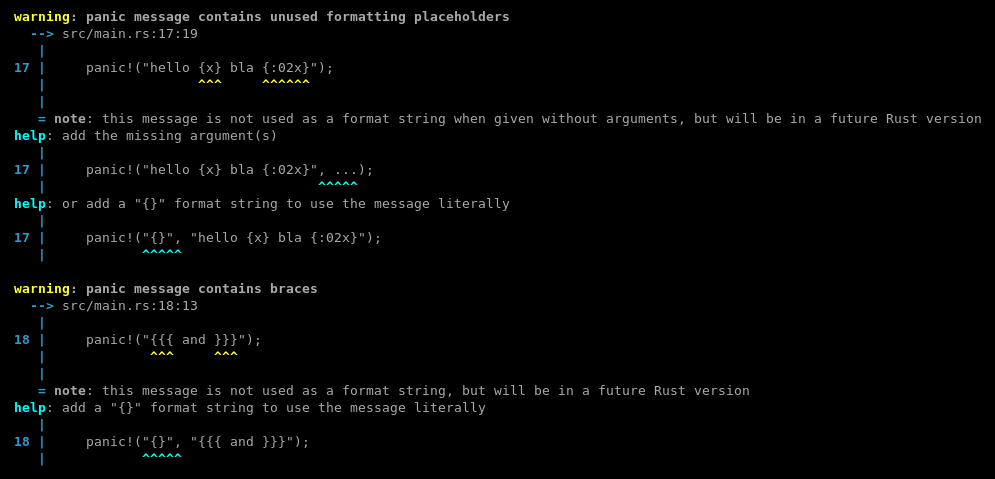
This lint is also a good starting point for adding warnings about `panic!(not_a_string)` later, once [`panic_any()`](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/74622) becomes a stable alternative.
Fix typo in `std::io::Write` docs
These referred to a “`Write`er”—extra *e*. Presumably a copy-paste
holdover from “`Read`er”.
Test Plan:
Running ``git grep '`\?[Ww]rite`\?er'`` no longer finds any results.
wchargin-branch: io-write-docs
Tighten the bounds on atomic Ordering in std::sys::unix::weak::Weak
This moves reading this from multiple SeqCst reads to Relaxed read + Acquire fence if we are actually going to use the data.
Would love to avoid the Acquire fence, but doing so would need Ordering::Consume, which neither Rust, nor LLVM supports (a shame, since this fence is hardly free on ARM, which is what I was hoping to improve).
r? ``@Amanieu`` (Sorry for always picking you, but I know a lot of people wouldn't feel comfortable reviewing atomic ordering changes)
linux: try to use libc getrandom to allow interposition
We'll try to use a weak `getrandom` symbol first, because that allows
things like `LD_PRELOAD` interposition. For example, perf measurements
might want to disable randomness to get reproducible results. If the
weak symbol is not found, we fall back to a raw `SYS_getrandom` call.
Updated the list of white-listed target features for x86
This PR both adds in-source documentation on what to look out for when adding a new (X86) feature set and [adds all that are detectable at run-time in Rust stable as of 1.27.0](https://github.com/rust-lang/stdarch/blob/master/crates/std_detect/src/detect/arch/x86.rs).
This should only enable the use of the corresponding LLVM intrinsics.
Actual intrinsics need to be added separately in rust-lang/stdarch.
It also re-orders the run-time-detect test statements to be more consistent
with the actual list of intrinsics whitelisted and removes underscores not present
in the actual names (which might be mistaken as being part of the name)
The reference for LLVM's feature names used is [this file](https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/blob/master/llvm/include/llvm/Support/X86TargetParser.def).
This PR was motivated as the compiler end's part for allowing #67329 to be adressed over on rust-lang/stdarch
These referred to a “`Write`er”—extra *e*. Presumably a copy-paste
holdover from “`Read`er”.
Test Plan:
Running ``git grep '`\?[Ww]rite`\?er'`` no longer finds any results.
wchargin-branch: io-write-docs
Rollup of 9 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #77939 (Ensure that the source code display is working with DOS backline)
- #78138 (Upgrade dlmalloc to version 0.2)
- #78967 (Make codegen tests compatible with extra inlining)
- #79027 (Limit storage duration of inlined always live locals)
- #79077 (document that __rust_alloc is also magic to our LLVM fork)
- #79088 (clarify `span_label` documentation)
- #79097 (Code block invalid html tag lint)
- #79105 (std: Fix test `symlink_hard_link` on Windows)
- #79107 (build-manifest: strip newline from rustc version)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
`@rustbot` modify labels: rollup
std: Fix test `symlink_hard_link` on Windows
The test was introduced in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/78026 and fails depending on Windows version and admin rights.
Other similar tests check for symlink creation permissions before doing anything, this PR performs the same check for `symlink_hard_link` as well.
Upgrade dlmalloc to version 0.2
In preparation of adding dynamic memory management support for SGXv2-enabled platforms, the dlmalloc crate has been refactored. More specifically, support has been added to implement platform specification outside of the dlmalloc crate. (see https://github.com/alexcrichton/dlmalloc-rs/pull/15)
This PR upgrades dlmalloc to version 0.2 for the `wasm` and `sgx` targets.
As the dlmalloc changes have received a positive review, but have not been merged yet, this PR contains a commit to prevent tidy from aborting CI prematurely.
cc: `@jethrogb`
Make the libstd build script smaller
Of all sysroot crates currently only compiler_builtins, miniz_oxide and std require a build script. compiler_builtins uses to conditionally enable certain features and possibly compile a C version ([source](63ccaf11f0/build.rs)), miniz_oxide only uses it to detect if liballoc is supported as the MSRV is 1.34.0 instead of the 1.36.0 which stabilized liballoc ([source](28514ec09f/miniz_oxide/build.rs)). std now only uses it to enable `freebsd12` when the `RUST_STD_FREEBSD_12_ABI` env var is set, to determine if `restricted-std` should be set, to set the `STD_ENV_ARCH` env var identical to `CARGO_CFG_TARGET_ARCH`, and to unconditionally enable `backtrace_in_libstd`.
If all build scripts were to be removed, it would be possible for rustc to completely compile it's own sysroot. It currently requires a rustc version that already has an available libstd to compile the build scripts. If rustc can completely compile it's own sysroot, rustbuild could be simplified to not forcefully use the bootstrap compiler for build scripts.
`@rustbot` modify labels: +T-compiler +libs-impl
We'll try to use a weak `getrandom` symbol first, because that allows
things like `LD_PRELOAD` interposition. For example, perf measurements
might want to disable randomness to get reproducible results. If the
weak symbol is not found, we fall back to a raw `SYS_getrandom` call.
Simplify output capturing
This is a sequence of incremental improvements to the unstable/internal `set_panic` and `set_print` mechanism used by the `test` crate:
1. Remove the `LocalOutput` trait and use `Arc<Mutex<dyn Write>>` instead of `Box<dyn LocalOutput>`. In practice, all implementations of `LocalOutput` were just `Arc<Mutex<..>>`. This simplifies some logic and removes all custom `Sink` implementations such as `library/test/src/helpers/sink.rs`. Also removes a layer of indirection, as the outermost `Box` is now gone. It also means that locking now happens per `write_fmt`, not per individual `write` within. (So `"{} {}\n"` now results in one `lock()`, not four or more.)
2. Since in all cases the `dyn Write`s were just `Vec<u8>`s, replace the type with `Arc<Mutex<Vec<u8>>>`. This simplifies things more, as error handling and flushing can be removed now. This also removes the hack needed in the default panic handler to make this work with `::realstd`, as (unlike `Write`) `Vec<u8>` is from `alloc`, not `std`.
3. Replace the `RefCell`s by regular `Cell`s. The `RefCell`s were mostly used as `mem::replace(&mut *cell.borrow_mut(), something)`, which is just `Cell::replace`. This removes an unecessary bookkeeping and makes the code a bit easier to read.
4. Merge `set_panic` and `set_print` into a single `set_output_capture`. Neither the test crate nor rustc (the only users of this feature) have a use for using these separately. Merging them simplifies things even more. This uses a new function name and feature name, to make it clearer this is internal and not supposed to be used by other crates.
Might be easier to review per commit.
Rename/Deprecate LayoutErr in favor of LayoutError
Implements rust-lang/wg-allocators#73.
This patch renames LayoutErr to LayoutError, and uses a type alias to support users using the old name.
The new name will be instantly stable in release 1.49 (current nightly), the type alias will become deprecated in release 1.51 (so that when the current nightly is 1.51, 1.49 will be stable).
This is the only error type in `std` that ends in `Err` rather than `Error`, if this PR lands all stdlib error types will end in `Error` 🥰
Fix an intrinsic invocation on threaded wasm
This looks like it was forgotten to get updated in #74482 and wasm with
threads isn't built on CI so we didn't catch this by accident.
specialize io::copy to use copy_file_range, splice or sendfile
Fixes#74426.
Also covers #60689 but only as an optimization instead of an official API.
The specialization only covers std-owned structs so it should avoid the problems with #71091
Currently linux-only but it should be generalizable to other unix systems that have sendfile/sosplice and similar.
There is a bit of optimization potential around the syscall count. Right now it may end up doing more syscalls than the naive copy loop when doing short (<8KiB) copies between file descriptors.
The test case executes the following:
```
[pid 103776] statx(3, "", AT_STATX_SYNC_AS_STAT|AT_EMPTY_PATH, STATX_ALL, {stx_mask=STATX_ALL|STATX_MNT_ID, stx_attributes=0, stx_mode=S_IFREG|0644, stx_size=17, ...}) = 0
[pid 103776] write(4, "wxyz", 4) = 4
[pid 103776] write(4, "iklmn", 5) = 5
[pid 103776] copy_file_range(3, NULL, 4, NULL, 5, 0) = 5
```
0-1 `stat` calls to identify the source file type. 0 if the type can be inferred from the struct from which the FD was extracted
𝖬 `write` to drain the `BufReader`/`BufWriter` wrappers. only happen when buffers are present. 𝖬 ≾ number of wrappers present. If there is a write buffer it may absorb the read buffer contents first so only result in a single write. Vectored writes would also be an option but that would require more invasive changes to `BufWriter`.
𝖭 `copy_file_range`/`splice`/`sendfile` until file size, EOF or the byte limit from `Take` is reached. This should generally be *much* more efficient than the read-write loop and also have other benefits such as DMA offload or extent sharing.
## Benchmarks
```
OLD
test io::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy ... bench: 21,002 ns/iter (+/- 750) = 6240 MB/s [ext4]
test io::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy ... bench: 35,704 ns/iter (+/- 1,108) = 3671 MB/s [btrfs]
test io::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy ... bench: 57,002 ns/iter (+/- 4,205) = 2299 MB/s
test io::tests::bench_socket_pipe_socket_copy ... bench: 142,640 ns/iter (+/- 77,851) = 918 MB/s
NEW
test io::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy ... bench: 14,745 ns/iter (+/- 519) = 8889 MB/s [ext4]
test io::tests::bench_file_to_file_copy ... bench: 6,128 ns/iter (+/- 227) = 21389 MB/s [btrfs]
test io::tests::bench_file_to_socket_copy ... bench: 13,767 ns/iter (+/- 3,767) = 9520 MB/s
test io::tests::bench_socket_pipe_socket_copy ... bench: 26,471 ns/iter (+/- 6,412) = 4951 MB/s
```
Previously EOVERFLOW handling was only applied for io::copy specialization
but not for fs::copy sharing the same code.
Additionally we lower the chunk size to 1GB since we have a user report
that older kernels may return EINVAL when passing 0x8000_0000
but smaller values succeed.