Deny broken intra-doc links in linkchecker
Since rustdoc isn't warning about these links, check for them manually.
This also fixes the broken links that popped up from the lint.
Remove arena's dependency on `rustc_data_structures`
`rustc_arena` currently has a dependency on `rustc_data_structures` because of a trivial "don't inline me" function. This PR copies that function and removes the dependency.
The primary motivation is to get the changes from
https://github.com/tokio-rs/tracing/pull/990. Example output:
```
$ RUSTDOC_LOG=debug rustdoc +rustc2
warning: some trace filter directives would enable traces that are disabled statically
| `debug` would enable the DEBUG level for all targets
= note: the static max level is `info`
= help: to enable DEBUG logging, remove the `max_level_info` feature
```
- Remove useless test
This was testing for an ICE when passing `RUST_LOG=rustc_middle`. I
noticed it because it started giving the tracing warning (because tests
are not run with debug-logging enabled). Since this bug seems unlikely
to re-occur, I just removed it altogether.
Rollup of 11 pull requests
Successful merges:
- #76784 (Add some docs to rustdoc::clean::inline and def_id functions)
- #76911 (fix VecDeque::iter_mut aliasing issues)
- #77400 (Fix suggestions for x.py setup)
- #77515 (Update to chalk 0.31)
- #77568 (inliner: use caller param_env)
- #77571 (Use matches! for core::char methods)
- #77582 (Move `EarlyOtherwiseBranch` to mir-opt-level 2)
- #77590 (Update RLS and Rustfmt)
- #77605 (Fix rustc_def_path to show the full path and not the trimmed one)
- #77614 (Let backends access span information)
- #77624 (Add c as a shorthand check alternative for new options #77603)
Failed merges:
r? `@ghost`
Support static linking with glibc and target-feature=+crt-static
With this change, it's possible to build on a linux-gnu target and pass
RUSTFLAGS='-C target-feature=+crt-static' or the equivalent via a
`.cargo/config.toml` file, and get a statically linked executable.
Update to libc 0.2.78, which adds support for static linking with glibc.
Add `crt_static_respected` to the `linux_base` target spec.
Update `android_base` and `linux_musl_base` accordingly. Avoid enabling
crt_static_respected on Android platforms, since that hasn't been
tested.
Closes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/65447.
This is a combination of 18 commits.
Commit #2:
Additional examples and some small improvements.
Commit #3:
fixed mir-opt non-mir extensions and spanview title elements
Corrected a fairly recent assumption in runtest.rs that all MIR dump
files end in .mir. (It was appending .mir to the graphviz .dot and
spanview .html file names when generating blessed output files. That
also left outdated files in the baseline alongside the files with the
incorrect names, which I've now removed.)
Updated spanview HTML title elements to match their content, replacing a
hardcoded and incorrect name that was left in accidentally when
originally submitted.
Commit #4:
added more test examples
also improved Makefiles with support for non-zero exit status and to
force validation of tests unless a specific test overrides it with a
specific comment.
Commit #5:
Fixed rare issues after testing on real-world crate
Commit #6:
Addressed PR feedback, and removed temporary -Zexperimental-coverage
-Zinstrument-coverage once again supports the latest capabilities of
LLVM instrprof coverage instrumentation.
Also fixed a bug in spanview.
Commit #7:
Fix closure handling, add tests for closures and inner items
And cleaned up other tests for consistency, and to make it more clear
where spans start/end by breaking up lines.
Commit #8:
renamed "typical" test results "expected"
Now that the `llvm-cov show` tests are improved to normally expect
matching actuals, and to allow individual tests to override that
expectation.
Commit #9:
test coverage of inline generic struct function
Commit #10:
Addressed review feedback
* Removed unnecessary Unreachable filter.
* Replaced a match wildcard with remining variants.
* Added more comments to help clarify the role of successors() in the
CFG traversal
Commit #11:
refactoring based on feedback
* refactored `fn coverage_spans()`.
* changed the way I expand an empty coverage span to improve performance
* fixed a typo that I had accidently left in, in visit.rs
Commit #12:
Optimized use of SourceMap and SourceFile
Commit #13:
Fixed a regression, and synched with upstream
Some generated test file names changed due to some new change upstream.
Commit #14:
Stripping out crate disambiguators from demangled names
These can vary depending on the test platform.
Commit #15:
Ignore llvm-cov show diff on test with generics, expand IO error message
Tests with generics produce llvm-cov show results with demangled names
that can include an unstable "crate disambiguator" (hex value). The
value changes when run in the Rust CI Windows environment. I added a sed
filter to strip them out (in a prior commit), but sed also appears to
fail in the same environment. Until I can figure out a workaround, I'm
just going to ignore this specific test result. I added a FIXME to
follow up later, but it's not that critical.
I also saw an error with Windows GNU, but the IO error did not
specify a path for the directory or file that triggered the error. I
updated the error messages to provide more info for next, time but also
noticed some other tests with similar steps did not fail. Looks
spurious.
Commit #16:
Modify rust-demangler to strip disambiguators by default
Commit #17:
Remove std::process::exit from coverage tests
Due to Issue #77553, programs that call std::process::exit() do not
generate coverage results on Windows MSVC.
Commit #18:
fix: test file paths exceeding Windows max path len
Improve build-manifest to work with the improved promote-release
This PR makes some changes to build-manifest to have it work better with the other improvements I'm making to [promote-release](https://github.com/rust-lang/promote-release).
A new way to invoke the tool was added: `./x.py run src/tools/build-manifest`. The new invocation disables the generation of `.sha256` files and the generation of GPG signatures, as those steps are not tied to the Rust version we're building the manifest of: handling them in `promote-release` will improve the maintenability of our release process. Invocations through the old command (`./x.py dist hash-and-sign`) are referred inside the source code as "legacy". The new invocation also enables internal parallelism, disabled on legacy to avoid overloading our old server.
Improvements were also made on how the checksums included in the manifest are generated:
* The manifest is first generated with placeholder checksums, and then a function walks through the manifes and calculates only the needed hashes. Before this PR, all the hashes were calculated beforehand, including the hashes of unused files.
* Calculating the hashes is now done in parallel with rayon, to better utilize all the available disk bandwidth.
* The `sha2` crate is now used instead of the `sha256sum` CLI tool: this avoids the overhead of calling another process, but more importantly enables hardware acceleration whenever available (the `sha256sum` CLI tool doesn't support it at all).
r? @Mark-Simulacrum
This PR is best reviewed commit-by-commit.
Use `tracing` spans to trace the entire MIR interp stack
r? @RalfJung
While being very verbose, this allows really good tracking of what's going on. While I considered schemes like the previous indenter that we had (which we could get by using the `tracing-tree` crate), this will break down horribly with things like multithreaded rustc. Instead, we can now use `RUSTC_LOG` to restrict the things being traced. You could specify a filter in a way that only shows the logging of a specific frame.
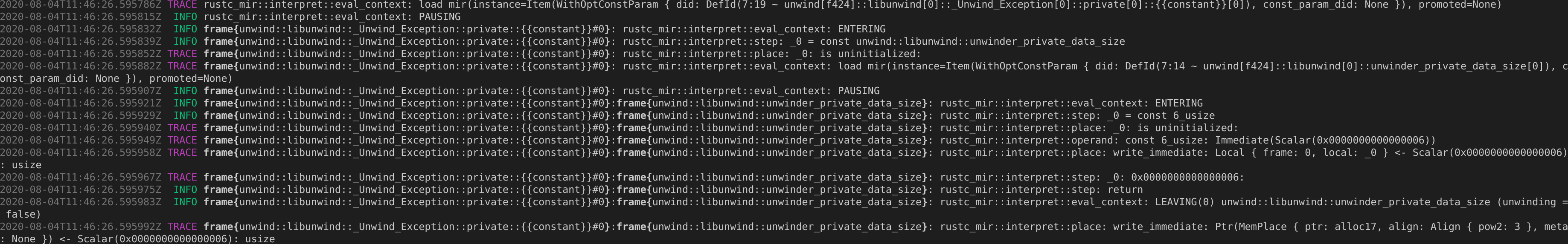
If we lower the span's level to `debug`, then in `info` level logging we'd not see the frames, but in `debug` level we would see them. The filtering rules in `tracing` are super powerful, but I'm not sure if we can specify a filter so we do see `debug` level events, but *not* the `frame` spans. The documentation at https://docs.rs/tracing-subscriber/0.2.10/tracing_subscriber/struct.EnvFilter.html makes me think that we can only turn on things, not turn off things at a more precise level.
cc @hawkw
This commit improves the way build-manifest calculates the checksums
included in the manifest, speeding it up:
* Instead of calculating all the hashes beforehand and then using the
ones we need, the manifest is first generated with placeholder hashes,
and then a function walks through the manifest and calculates only the
needed checksums.
* Calculating the checksums is now done in parallel with rayon, to
better utilize all the available disk bandwidth.
* Calculating the checksums now uses the sha2 crate instead of the
sha256sum CLI tool: this avoids the overhead of calling another
process, but more importantly uses hardware acceleration whenever
available (the CLI tool doesn't support it at all).
Refactor versions detection in build-manifest
This PR refactors how `build-manifest` handles versions, making the following changes:
* `build-manifest` now detects the "package releases" on its own, without relying on rustbuild providing them through CLI arguments. This drastically simplifies calling the tool outside of `x.py`, and will allow to ship the prebuilt tool in a tarball in the future, with the goal of stopping to invoke `x.py` during `promote-release`.
* The `tar` command is not used to extract the version and the git hash from tarballs anymore. The `flate2` and `tar` crates are used instead. This makes detecting those pieces of data way faster, as the archive is decompressed just once and we stop parsing the archive once all the information is retrieved.
* The code to extract the version and the git hash now stores all the collected data dynamically, without requiring to add new fields to the `Builder` struct every time.
I tested the changes locally and it should behave the same as before.
r? `@Mark-Simulacrum`
Small improvements in liveness pass
* Remove redundant debug logging (`add_variable` already contains logging).
* Remove redundant fields for a number of live nodes and variables.
* Delay conversion from a symbol to a string until linting.
* Inline contents of specials struct.
* Remove unnecessary local variable exit_ln.
* Use newtype_index for Variable and LiveNode.
* Access live nodes directly through self.lnks[ln].
No functional changes intended (except those related to the logging).
Make `ensure_sufficient_stack()` non-generic, using cargo-llvm-lines
Inspired by [this blog post](https://blog.mozilla.org/nnethercote/2020/08/05/how-to-speed-up-the-rust-compiler-some-more-in-2020/) from `@nnethercote,` I used [cargo-llvm-lines](https://github.com/dtolnay/cargo-llvm-lines/) on the rust compiler itself, to improve it's compile time. This PR contains only one low-hanging fruit, but I also want to share some measurements.
The function `ensure_sufficient_stack()` was monomorphized 1500 times, and with it the `stacker` and `psm` crates, for a total of 1.5% of all llvm IR lines. With some trickery I convert the generic closure into a dynamic one, and thus all that code is only monomorphized once.
# Measurements
Getting these numbers took some fiddling with CLI flags and I [modified](https://github.com/Julian-Wollersberger/cargo-llvm-lines/blob/master/src/main.rs#L115) cargo-llvm-lines to read from a folder instead of invoking cargo. Commands I used:
```
./x.py clean
RUSTFLAGS="--emit=llvm-ir -C link-args=-fuse-ld=lld -Z self-profile=profile" CARGOFLAGS_BOOTSTRAP="-Ztimings" RUSTC_BOOTSTRAP=1 ./x.py build -i --stage 1 library/std
# Then manually copy all .ll files into a folder I hardcoded in cargo-llvm-lines in main.rs#L115
cd ../cargo-llvm-lines
cargo run llvm-lines
```
The result is this list (see [first 500 lines](https://github.com/Julian-Wollersberger/cargo-llvm-lines/blob/master/llvm-lines-rustc-before.txt) ), before the change:
```
Lines Copies Function name
----- ------ -------------
16894211 (100%) 58417 (100%) (TOTAL)
2223855 (13.2%) 502 (0.9%) rustc_query_system::query::plumbing::get_query_impl::{{closure}}
1331918 (7.9%) 1287 (2.2%) hashbrown::raw::RawTable<T>::reserve_rehash
774434 (4.6%) 12043 (20.6%) core::ptr::drop_in_place
294170 (1.7%) 499 (0.9%) rustc_query_system::dep_graph::graph::DepGraph<K>::with_task_impl
245410 (1.5%) 1552 (2.7%) psm::on_stack::with_on_stack
210311 (1.2%) 1 (0.0%) rustc_target::spec::load_specific
200962 (1.2%) 513 (0.9%) rustc_query_system::query::plumbing::get_query_impl
190704 (1.1%) 1 (0.0%) rustc_middle::ty::query::<impl rustc_middle::ty::context::TyCtxt>::alloc_self_profile_query_strings
180272 (1.1%) 468 (0.8%) rustc_query_system::query::plumbing::load_from_disk_and_cache_in_memory
177396 (1.1%) 114 (0.2%) rustc_query_system::query::plumbing::force_query_impl
161134 (1.0%) 445 (0.8%) rustc_query_system::dep_graph::graph::DepGraph<K>::with_anon_task
141551 (0.8%) 186 (0.3%) rustc_query_system::query::plumbing::incremental_verify_ich
110191 (0.7%) 7 (0.0%) rustc_middle::ty::context::_DERIVE_rustc_serialize_Decodable_D_FOR_TypeckResults::<impl rustc_serialize::serialize::Decodable<__D> for rustc_middle::ty::context::TypeckResults>::decode::{{closure}}
108590 (0.6%) 420 (0.7%) core::ops::function::FnOnce::call_once
88488 (0.5%) 21 (0.0%) rustc_query_system::dep_graph::graph::DepGraph<K>::try_mark_previous_green
86368 (0.5%) 1 (0.0%) rustc_middle::ty::query::stats::query_stats
85654 (0.5%) 3973 (6.8%) <&T as core::fmt::Debug>::fmt
84475 (0.5%) 1 (0.0%) rustc_middle::ty::query::Queries::try_collect_active_jobs
81220 (0.5%) 862 (1.5%) <hashbrown::raw::RawIterHash<T> as core::iter::traits::iterator::Iterator>::next
77636 (0.5%) 54 (0.1%) core::slice::sort::recurse
66484 (0.4%) 461 (0.8%) <hashbrown::raw::RawIter<T> as core::iter::traits::iterator::Iterator>::next
```
All `.ll` files together had 4.4GB. After my change they had 4.2GB. So a few percent less code LLVM has to process. Hurray!
Sadly, I couldn't measure an actual wall-time improvement. Watching YouTube while compiling added to much noise...
Here is the top of the list after the change:
```
16460866 (100%) 58341 (100%) (TOTAL)
1903085 (11.6%) 504 (0.9%) rustc_query_system::query::plumbing::get_query_impl::{{closure}}
1331918 (8.1%) 1287 (2.2%) hashbrown::raw::RawTable<T>::reserve_rehash
777796 (4.7%) 12031 (20.6%) core::ptr::drop_in_place
551462 (3.4%) 1519 (2.6%) rustc_data_structures::stack::ensure_sufficient_stack::{{closure}}
```
Note that the total was reduced by 430 000 lines and `psm::on_stack::with_on_stack` has disappeared. Instead `rustc_data_structures::stack::ensure_sufficient_stack::{{closure}}` appeared. I'm confused about that one, but it seems to consist of inlined calls to `rustc_query_system::*` stuff.
Further note the other two big culprits in this list: `rustc_query_system` and `hashbrown`. These two are monomorphized many times, the query system summing to more than 20% of all lines, not even counting code that's probably inlined elsewhere.
Assuming compile times scale linearly with llvm-lines, that means a possible 20% compile time reduction.
Reducing eg. `get_query_impl` would probably need a major refactoring of the qery system though. _Everything_ in there is generic over multiple types, has associated types and passes generic Self arguments by value. Which means you can't simply make things `dyn`.
---------------------------------------
This PR is a small step to make rustc compile faster and thus make contributing to rustc less painful. Nonetheless I love Rust and I find the work around rustc fascinating :)