On Fuchsia, spawning a subprocess does not automatically
clone all of the parent process' capabilities. UTC time on
Fuchsia is managed by a top-level userspace clock capability
that is cloned and passed to subprocesses.
This change ensures that any Rust subprocess gets access to the
UTC clock, if the parent had access to it. This is critical for
tests, which on Fuchsia, use panic=abort and spawn subprocesses
per test.
Update stdarch
This PR **changes the public signature** of the following functions in `core::arch::{x86, x86_64}`:
```patch
-pub unsafe fn _mm256_extract_epi8(a: __m256i, imm8: i32) -> i8
+pub unsafe fn _mm256_extract_epi8(a: __m256i, imm8: i32) -> i32
-pub unsafe fn _mm256_extract_epi16(a: __m256i, imm8: i32) -> i16
+pub unsafe fn _mm256_extract_epi16(a: __m256i, imm8: i32) -> i32
```
This change is desired so that these signatures
* are similar to those of the 128-bit versions `_mm_extract_epi8` and `_mm_extract_epi16`
* match the Intel definitions for the intrinsics
* [RFC 2325](https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/blob/master/text/2325-stable-simd.md) specifies that the exact vendor function signatures should be used
A [crater run](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/73166#issuecomment-667230319) revealed only a single breakage. The [vektor crate](https://github.com/AdamNiederer/vektor/blob/master/src/x86/avx2.rs#L2436-L2472) copied the incorrect signatures in `core` exactly to their own crate. The functions don't seem to be used by anyone anywhere.
Actual breakage is not expected, since due to the nature of the functions, users would generally write `_mm256_extract_epi8(...) as u8` or `_mm256_extract_epi16(...) as u16`.
See https://github.com/rust-lang/stdarch/pull/868/. Note that the changes from that stdarch PR have already partially landed in core after https://github.com/rust-lang/stdarch/pull/878/. This PR is now only about the remaining changes.
Implementation of peer credentials for Unix sockets
The code in `ucred.rs` is based on the work done in [PR 13](https://github.com/tokio-rs/tokio-uds/pull/13) in the tokio-uds repository on GitHub.
This commit is effectively a port to the stdlib, so credit to Martin Habovštiak (`@Kixunil)` and contributors for the meat of this work. 🥇
Happy to make changes as needed. 🙂
Split `core::slice` to smaller mods
Unfortunately the `#[lang = "slice"]` is too big (3003 lines), I cannot split it further.
Note for reviewer:
* I split to multiple commits for easier reviewing, but I could git squash them all to one if requested.
* Recommend pulling this change locally and using advanced git diff viewer or this command:
```
git show --reverse --color-moved=dimmed-zebra master..
```
---
I split core/slice/mod.rs to these modules:
* `ascii`: For operations on `[u8]`.
* `cmp`: For comparison operations on `[T]`, like PartialEq and SliceContains impl.
* `index`: For indexing operations like Index/IndexMut and SliceIndex.
* `iter`: For Iterator definitions and implementation on `[T]`.
- `macros`: For iterator! and forward_iterator! macros.
* `raw`: For free function to create `&[T]` or `&mut [T]` from pointer + length or a reference.
The heapsort wrapper in mod.rs is removed in favor of reexport from `sort::heapsort`.
Optimize behavior of vec.split_off(0) (take all)
Optimization improvement to `split_off()` so the performance meets the
intuitively expected behavior when `at == 0`, avoiding the current behavior
of copying the entire vector.
The change honors documented behavior that the original vector's
"previous capacity unchanged".
This improvement better supports the pattern for building and flushing a
buffer of elements, such as the following:
```rust
let mut vec = Vec::new();
loop {
vec.push(something);
if condition_is_met {
process(vec.split_off(0));
}
}
```
`Option` wrapping is the first alternative I thought of, but is much
less obvious and more verbose:
```rust
let mut capacity = 1;
let mut vec: Option<Vec<Stuff>> = None;
loop {
vec.get_or_insert_with(|| Vec::with_capacity(capacity)).push(something);
if condition_is_met {
capacity = vec.capacity();
process(vec.take().unwrap());
}
}
```
Directly using `mem::replace()` (instead of calling`split_off()`) could work,
but `mem::replace()` is a more advanced tool for Rust developers, and in
this case, I believe developers would assume the standard library should
be sufficient for the purpose described here.
The benefit of the approach to this change is it does not change the
existing API contract, but improves the peformance of `split_off(0)` for
`Vec`, `String` (which delegates `split_off()` to `Vec`), and any other
existing use cases.
This change adds tests to validate the behavior of `split_off()` with
regard to capacity, as originally documented, and confirm that behavior
still holds, when `at == 0`.
The change is an implementation detail, and does not require a
documentation change, but documenting the new behavior as part of its
API contract may benefit future users.
(Let me know if I should make that documentation update.)
Note, for future consideration:
I think it would be helpful to introduce an additional method to `Vec`
(if not also to `String`):
```
pub fn take_all(&mut self) -> Self {
self.split_off(0)
}
```
This would make it more clear how `Vec` supports the pattern, and make
it easier to find, since the behavior is similar to other `take()`
methods in the Rust standard library.
r? `@wesleywiser`
FYI: `@tmandry`
The code in `ucred.rs` is based on the work done in PR 13 in the
tokio-uds repository on GitHub. Link below for reference:
https://github.com/tokio-rs/tokio-uds/pull/13
Credit to Martin Habovštiak (GitHub username Kixunil) and contributors
for this work!
Optimization improvement to `split_off()` so the performance meets the
intuitively expected behavior when `at == 0`, avoiding the current
behavior of copying the entire vector.
The change honors documented behavior that the method leaves the
original vector's "previous capacity unchanged".
This improvement better supports the pattern for building and flushing a
buffer of elements, such as the following:
```rust
let mut vec = Vec::new();
loop {
vec.push(something);
if condition_is_met {
process(vec.split_off(0));
}
}
```
`Option` wrapping is the first alternative I thought of, but is much
less obvious and more verbose:
```rust
let mut capacity = 1;
let mut vec: Option<Vec<Stuff>> = None;
loop {
vec.get_or_insert_with(|| Vec::with_capacity(capacity)).push(something);
if condition_is_met {
capacity = vec.capacity();
process(vec.take().unwrap());
}
}
```
Directly applying `mem::replace()` could work, but `mem::` functions are
typically a last resort, when a developer is actively seeking better
performance than the standard library provides, for example.
The benefit of the approach to this change is it does not change the
existing API contract, but improves the peformance of `split_off(0)` for
`Vec`, `String` (which delegates `split_off()` to `Vec`), and any other
existing use cases.
This change adds tests to validate the behavior of `split_off()` with
regard to capacity, as originally documented, and confirm that behavior
still holds, when `at == 0`.
The change is an implementation detail, and does not require a
documentation change, but documenting the new behavior as part of its
API contract may benefit future users.
(Let me know if I should make that documentation update.)
Note, for future consideration:
I think it would be helpful to introduce an additional method to `Vec`
(if not also to `String`):
```
pub fn take_all(&mut self) -> Self {
self.split_off(0)
}
```
This would make it more clear how `Vec` supports the pattern, and make
it easier to find, since the behavior is similar to other `take()`
methods in the Rust standard library.
Remove internal and unstable MaybeUninit::UNINIT.
Looks like it is no longer necessary, as `uninit_array()` can be used instead in the few cases where it was needed.
(I wanted to just add `#[doc(hidden)]` to remove clutter from the documentation, but looks like it can just be removed entirely.)
Make the following methods unstable const under the `const_pin` feature:
- `new`
- `new_unchecked`
- `into_inner`
- `into_inner_unchecked`
- `get_ref`
- `into_ref`
Also adds tests for these methods in a const context.
Tracking issue: #76654
- Move `held` into the boxed part, since the SRW lock implementation
does not use this. This makes the Mutex 50% smaller.
- Use `Cell` instead of `UnsafeCell` for `held`, such that `.replace()`
can be used.
- Add some comments.
Warn for #[unstable] on trait impls when it has no effect.
Earlier today I sent a PR with an `#[unstable]` attribute on a trait `impl`, but was informed that this attribute has no effect there. (comment: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/76525#issuecomment-689678895, issue: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/55436)
This PR adds a warning for this situation. Trait `impl` blocks with `#[unstable]` where both the type and the trait are stable will result in a warning:
```
warning: An `#[unstable]` annotation here has no effect. See issue #55436 <https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/55436> for more information.
--> library/std/src/panic.rs:235:1
|
235 | #[unstable(feature = "integer_atomics", issue = "32976")]
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
```
---
It detects three problems in the existing code:
1. A few `RefUnwindSafe` implementations for the atomic integer types in `library/std/src/panic.rs`. Example:
d92155bf6a/library/std/src/panic.rs (L235-L236)
2. An implementation of `Error` for `LayoutErr` in `library/std/srd/error.rs`:
d92155bf6a/library/std/src/error.rs (L392-L397)
3. `From` implementations for `Waker` and `RawWaker` in `library/alloc/src/task.rs`. Example:
d92155bf6a/library/alloc/src/task.rs (L36-L37)
Case 3 interesting: It has a bound with an `#[unstable]` trait (`W: Wake`), so appears to have much effect on stable code. It does however break similar blanket implementations. It would also have immediate effect if `Wake` was implemented for any stable type. (Which is not the case right now, but there are no warnings in place to prevent it.) Whether this case is a problem or not is not clear to me. If it isn't, adding a simple `c.visit_generics(..);` to this PR will stop the warning for this case.
Make the following methods of `Duration` unstable const under `duration_const_2`:
- `from_secs_f64`
- `from_secs_f32`
- `mul_f64`
- `mul_f32`
- `div_f64`
- `div_f32`
This results in all methods of `Duration` being (unstable) const.
Also adds tests for these methods in a const context, moved the test to `library` as part of #76268.
Possible because of #72449, which made the relevant `f32` and `f64` methods const.
Tracking issue: #72440
Use IOV_MAX and UIO_MAXIOV constants in limit vectored I/O
Also updates the libc dependency to 0.2.77 (from 0.2.74) as the
constants were only recently added.
Related #68042, #75005
r? `@Amanieu` (also reviewed #75005)
Update `std::os` module documentation.
Adds missing descriptions for the modules `std::os::linux::fs` and `std::os::windows::io`.
Also adds punctuation for consistency with other descriptions.
Eliminate mut reference UB in Drop impl for Rc<T>
This changes `self.ptr.as_mut()` with `get_mut_unchecked` which
does not use an intermediate reference. Arc<T> already handled this
case properly.
Fixes#76509
Add MaybeUninit::assume_init_drop.
`ManuallyDrop`'s documentation tells the user to use `MaybeUninit` instead when handling uninitialized data. However, the main functionality of `ManuallyDrop` (`drop`) is not available directly on `MaybeUninit`. Adding it makes it easier to switch from one to the other.
I re-used the `maybe_uninit_extra` feature and tracking issue number (#63567), since it seems very related. (And to avoid creating too many features tracking issues for `MaybeUninit`.)
Add saturating methods for `Duration`
In some project, I needed a `saturating_add` method for `Duration`. I implemented it myself but i thought it would be a nice addition to the standard library as it matches closely with the integers types.
3 new methods have been introduced and are gated by the new `duration_saturating_ops` unstable feature:
* `Duration::saturating_add`
* `Duration::saturating_sub`
* `Duration::saturating_mul`
If have left the tracking issue to `none` for now as I want first to understand if those methods would be acceptable at all. If agreed, I'll update the PR with the tracking issue.
Further more, to match the behavior of integers types, I introduced 2 associated constants:
* `Duration::MIN`: this one is somehow a duplicate from `Duration::zero()` method, but at the time this method was added, `MIN` was rejected as it was considered a different semantic (see https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/72790#issuecomment-636511743).
* `Duration::MAX`
Both have been gated by the already existing unstable feature `duration_constants`, I can introduce a new unstable feature if needed or just re-use the `duration_saturating_ops`.
We might have to decide whether:
* `MIN` should be replaced by `ZERO`?
* associated constants over methods?
Add `slice::array_chunks_mut`
This follows `array_chunks` from #74373 with a mutable version, `array_chunks_mut`. The implementation is identical apart from mutability. The new tests are adaptations of the `chunks_exact_mut` tests, plus an inference test like the one for `array_chunks`.
I reused the unstable feature `array_chunks` and tracking issue #74985, but I can separate that if desired.
r? `@withoutboats`
cc `@lcnr`
Stabilize core::future::{pending,ready}
This PR stabilizes `core::future::{pending,ready}`, tracking issue https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/70921.
## Motivation
These functions have been on nightly for three months now, and have lived as part of the futures ecosystem for several years. In that time these functions have undergone several iterations, with [the `async-std` impls](https://docs.rs/async-std/1.6.2/async_std/future/index.html) probably diverging the most (using `async fn`, which in hindsight was a mistake).
It seems the space around these functions has been _thoroughly_ explored over the last couple of years, and the ecosystem has settled on the current shape of the functions. It seems highly unlikely we'd want to make any further changes to these functions, so I propose we stabilize.
## Implementation notes
This stabilization PR was fairly straightforward; this feature has already thoroughly been reviewed by the libs team already in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/70834. So all this PR does is remove the feature gate.
This impl was effectively stable. #[unstable] had no effect here,
since both Error and LayoutErr were already stable.
This effectively became stable as soon as LayoutErr became stable, which
was in 1.28.0.
These impls were effectively stable. #[unstable] had no effect here,
since both RefUnwindSafe and these types were already stable.
These effectively became stable as soon as the types became stable,
which was in 1.34.0.
Fixes#73268
When a deref coercion occurs, we may end up with a move error if the
base value has been partially moved out of. However, we do not indicate
anywhere that a deref coercion is occuring, resulting in an error
message with a confusing span.
This PR adds an explicit note to move errors when a deref coercion is
involved. We mention the name of the type that the deref-coercion
resolved to, as well as the `Deref::Target` associated type being used.
BTreeMap: move up reference to map's root from NodeRef
Since the introduction of `NodeRef` years ago, it also contained a mutable reference to the owner of the root node of the tree (somewhat disguised as *const). Its intent is to be used only when the rest of the `NodeRef` is no longer needed. Moving this to where it's actually used, thought me 2 things:
- Some sort of "postponed mutable reference" is required in most places that it is/was used, and that's exactly where we also need to store a reference to the length (number of elements) of the tree, for the same reason. The length reference can be a normal reference, because the tree code does not care about tree length (just length per node).
- It's downright obfuscation in `from_sorted_iter` (transplanted to #75329)
- It's one of the reasons for the scary notice on `reborrow_mut`, the other one being addressed in #73971.
This does repeat the raw pointer code in a few places, but it could be bundled up with the length reference.
r? `@Mark-Simulacrum`
Use intra-doc links in `core::ptr`
Part of #75080.
The only link that I did not change is a link to a function on the
`pointer` primitive because intra-doc links for the `pointer` primitive
don't work yet (see #63351).
---
@rustbot modify labels: A-intra-doc-links T-doc
Add drain_filter method to HashMap and HashSet
Add `HashMap::drain_filter` and `HashSet::drain_filter`, implementing part of rust-lang/rfcs#2140. These new methods are unstable. The tracking issue is #59618.
The added iterators behave the same as `BTreeMap::drain_filter` and `BTreeSet::drain_filter`, except their iteration order is arbitrary. The unit tests are adapted from `alloc::collections::btree`.
This branch rewrites `HashSet` to be a wrapper around `hashbrown::HashSet` rather than `std::collections::HashMap`.
(Both are themselves wrappers around `hashbrown::HashMap`, so the in-memory representation is the same either way.) This lets `std` re-use more iterator code from `hashbrown`. Without this change, we would need to duplicate much more code to implement `HashSet::drain_filter`.
This branch also updates the `hashbrown` crate to version 0.9.0. Aside from changes related to the `DrainFilter` iterators, this version only changes features that are not used in libstd or rustc. And it updates `indexmap` to version 1.6.0, whose only change is compatibility with `hashbrown` 0.9.0.
This avoids overlapping a reference covering the data field,
which may be changed due in concurrent conditions. This fully
fixed the UB mainfested with `new_cyclic`.
Since trait implementations cannot be unstable, we should only add them
when the as_str feature gets stabilized. Until then, only `.as_str()` is
available (behind a feature gate).
BTreeMap mutable iterators should not take any reference to visited nodes during iteration
Fixes#73915, overlapping mutable references during BTreeMap iteration
r? `@RalfJung`
The calling convention of pthread_getattr_np() is to initialize the
pthread_attr_t, so _destroy() is only necessary on success (and _init()
isn't necessary beforehand). On the other hand, FreeBSD wants the
attr_t to be initialized before pthread_attr_get_np(), and therefore it
should always be destroyed afterwards.
`write` is ambiguous because there's also a macro called `write`.
Also removed unnecessary and potentially confusing link to a function in
its own docs.
The only link that I did not change is a link to a function on the
`pointer` primitive because intra-doc links for the `pointer` primitive
don't work yet (see #63351).
ManuallyDrop's documentation tells the user to use MaybeUninit instead
when handling uninitialized data. However, the main functionality of
ManuallyDrop (drop) was not available directly on MaybeUninit. Adding it
makes it easier to switch from one to the other.
Implement Seek::stream_position() for BufReader
Optimization over `BufReader::seek()` for getting the current position without flushing the internal buffer.
Related to #31100. Based on the code in #70577.
Remove unneeded `#[cfg(not(test))]` from libcore
This fixes rust-analyzer inside these modules (currently it does not analyze them, assuming they're configured out).
Use ops::ControlFlow in rustc_data_structures::graph::iterate
Since I only know about this because you mentioned it,
r? @ecstatic-morse
If we're not supposed to use new `core` things in compiler for a while then feel free to close, but it felt reasonable to merge the two types since they're the same, and it might be convenient for people to use `?` in their traversal code.
(This doesn't do the type parameter swap; NoraCodes has signed up to do that one.)
time.rs: Make spelling of "Darwin" consistent
On line 89 of this file, the OS name is written as "Darwin", but on line 162 it is written in all-caps. Darwin is usually spelt as a standard proper noun, i.e. "Darwin", rather than in all-caps.
This change makes that form consistent in both places.
Indent a note to make folding work nicer
Sublime Text folds code based on indentation. It maybe an unnecessary change, but does it look nicer after that ?
Move various ui const tests to `library`
Move:
- `src\test\ui\consts\const-nonzero.rs` to `library\core`
- `src\test\ui\consts\ascii.rs` to `library\core`
- `src\test\ui\consts\cow-is-borrowed` to `library\alloc`
Part of #76268
r? @matklad
Make `Ipv4Addr` and `Ipv6Addr` const tests unit tests under `library`
These tests are about the standard library, not the compiler itself, thus should live in `library`, see #76268.
Move some Vec UI tests into alloc unit tests
A bit of work towards #76268, makes a number of the Vec UI tests that are simply running code into unit tests. Ensured that they are being run when testing liballoc locally.
Try to improve the documentation of `filter()` and `filter_map()`.
I believe the documentation is currently a little misleading.
For example, in the docs for `filter()`:
> If the closure returns `false`, it will try again, and call the closure on
> the next element, seeing if it passes the test.
This kind of implies that if the closure returns true then we *don't* "try
again" and no further elements are considered. In actuality that's not the
case, every element is tried regardless of what happened with the previous
element.
This change tries to clarify that by removing the uses of "try again"
altogether.
Use Arc::clone and Rc::clone in documentation
This PR replaces uses of `x.clone()` by `Rc::clone(&x)` (or `Arc::clone(&x)`) to better match the documentation for those types.
@rustbot modify labels: T-doc
rename MaybeUninit slice methods
The `first` methods conceptually point to the whole slice, not just its first element, so rename them to be consistent with the raw ptr methods on ref-slices.
Also, do the equivalent of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/76047 for the slice reference getters, and make them part of https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/63569 (so far they somehow had no tracking issue).
* first_ptr -> slice_as_ptr
* first_ptr_mut -> slice_as_mut_ptr
* slice_get_ref -> slice_assume_init_ref
* slice_get_mut -> slice_assume_init_mut
I believe the documentation is currently a little misleading.
For example, in the docs for `filter()`:
> If the closure returns `false`, it will try again, and call the closure on
> the next element, seeing if it passes the test.
This kind of implies that if the closure returns true then we *don't* "try
again" and no further elements are considered. In actuality that's not the
case, every element is tried regardless of what happened with the previous
element.
This change tries to clarify that by removing the uses of "try again"
altogether.
Enable some of profiler tests on Windows-gnu
CC https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/61266
Because of force-push GitHub didn't let me reopen https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/75184
Because of the GCC miscompilation, generated binaries either segfault or `.profraw` is malformed. Clang works fine but we can't use it on the CI.
However we can still test the IR for the proper instrumentation so let's do it.
BTreeMap: introduce marker::ValMut and reserve Mut for unique access
The mutable BTreeMap iterators (apart from `DrainFilter`) are double-ended, meaning they have to rely on a front and a back handle that each represent a reference into the tree. Reserve a type category `marker::ValMut` for them, so that we guarantee that they cannot reach operations on handles with borrow type `marker::Mut`and that these operations can assume unique access to the tree.
Including #75195, benchmarks report no genuine change:
```
benchcmp old new --threshold 5
name old ns/iter new ns/iter diff ns/iter diff % speedup
btree::map::iter_100 3,333 3,023 -310 -9.30% x 1.10
btree::map::range_unbounded_vs_iter 36,624 31,569 -5,055 -13.80% x 1.16
```
r? @Mark-Simulacrum
Respect `-Z proc-macro-backtrace` flag for panics inside libproc_macro
Fixes#76270
Previously, any panic occuring during a call to a libproc_macro method
(e.g. calling `Ident::new` with an invalid identifier) would always
cause an ICE message to be printed.
This is very similar to the existing `Box<[T; N]>: TryFrom<Box<[T]>>`, but allows avoiding the `shrink_to_fit` if you have a vector and not a boxed slice.
Move:
- `src\test\ui\consts\const-nonzero.rs` to `library\core`
- `src\test\ui\consts\ascii.rs` to `library\core`
- `src\test\ui\consts\cow-is-borrowed` to `library\alloc`
Part of #76268
specialize some collection and iterator operations to run in-place
This is a rebase and update of #66383 which was closed due inactivity.
Recent rustc changes made the compile time regressions disappear, at least for webrender-wrench. Running a stage2 compile and the rustc-perf suite takes hours on the hardware I have at the moment, so I can't do much more than that.
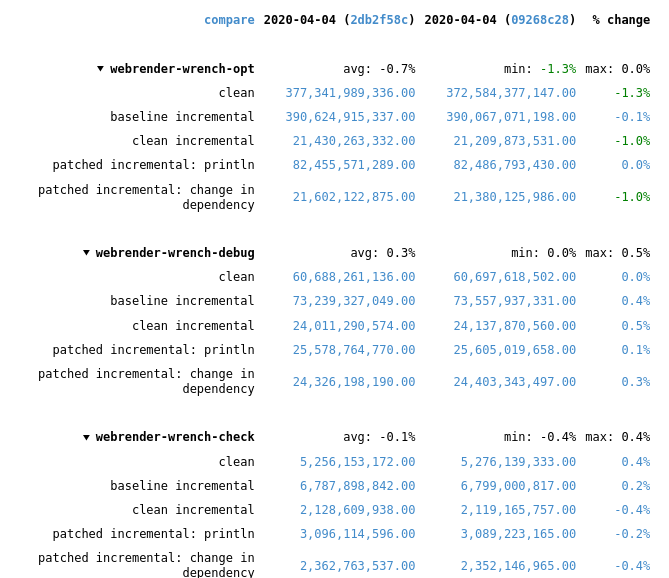
In the best case of the `vec::bench_in_place_recycle` synthetic microbenchmark these optimizations can provide a 15x speedup over the regular implementation which allocates a new vec for every benchmark iteration. [Benchmark results](https://gist.github.com/the8472/6d999b2d08a2bedf3b93f12112f96e2f). In real code the speedups are tiny, but it also depends on the allocator used, a system allocator that uses a process-wide mutex will benefit more than one with thread-local pools.
## What was changed
* `SpecExtend` which covered `from_iter` and `extend` specializations was split into separate traits
* `extend` and `from_iter` now reuse the `append_elements` if passed iterators are from slices.
* A preexisting `vec.into_iter().collect::<Vec<_>>()` optimization that passed through the original vec has been generalized further to also cover cases where the original has been partially drained.
* A chain of *Vec<T> / BinaryHeap<T> / Box<[T]>* `IntoIter`s through various iterator adapters collected into *Vec<U>* and *BinaryHeap<U>* will be performed in place as long as `T` and `U` have the same alignment and size and aren't ZSTs.
* To enable above specialization the unsafe, unstable `SourceIter` and `InPlaceIterable` traits have been added. The first allows reaching through the iterator pipeline to grab a pointer to the source memory. The latter is a marker that promises that the read pointer will advance as fast or faster than the write pointer and thus in-place operation is possible in the first place.
* `vec::IntoIter` implements `TrustedRandomAccess` for `T: Copy` to allow in-place collection when there is a `Zip` adapter in the iterator. TRA had to be made an unstable public trait to support this.
## In-place collectible adapters
* `Map`
* `MapWhile`
* `Filter`
* `FilterMap`
* `Fuse`
* `Skip`
* `SkipWhile`
* `Take`
* `TakeWhile`
* `Enumerate`
* `Zip` (left hand side only, `Copy` types only)
* `Peek`
* `Scan`
* `Inspect`
## Concerns
`vec.into_iter().filter(|_| false).collect()` will no longer return a vec with 0 capacity, instead it will return its original allocation. This avoids the cost of doing any allocation or deallocation but could lead to large allocations living longer than expected.
If that's not acceptable some resizing policy at the end of the attempted in-place collect would be necessary, which in the worst case could result in one more memcopy than the non-specialized case.
## Possible followup work
* split liballoc/vec.rs to remove `ignore-tidy-filelength`
* try to get trivial chains such as `vec.into_iter().skip(1).collect::<Vec<)>>()` to compile to a `memmove` (currently compiles to a pile of SIMD, see #69187 )
* improve up the traits so they can be reused by other crates, e.g. itertools. I think currently they're only good enough for internal use
* allow iterators sourced from a `HashSet` to be in-place collected into a `Vec`
The InPlaceIterable debug assert checks that the write pointer
did not advance beyond the read pointer. But TrustedRandomAccess
never advances the read pointer, thus triggering the assert.
Skip the assert if the source pointer did not change during iteration.
rustdoc: do not use plain summary for trait impls
Fixes#38386.
Fixes#48332.
Fixes#49430.
Fixes#62741.
Fixes#73474.
Unfortunately this is not quite ready to go because the newly-working links trigger a bunch of linkcheck failures. The failures are tough to fix because the links are resolved relative to the implementor, which could be anywhere in the module hierarchy.
(In the current docs, these links end up rendering as uninterpreted markdown syntax, so I don't think these failures are any worse than the status quo. It might be acceptable to just add them to the linkchecker whitelist.)
Ideally this could be fixed with intra-doc links ~~but it isn't working for me: I am currently investigating if it's possible to solve it this way.~~ Opened #73829.
EDIT: This is now ready!